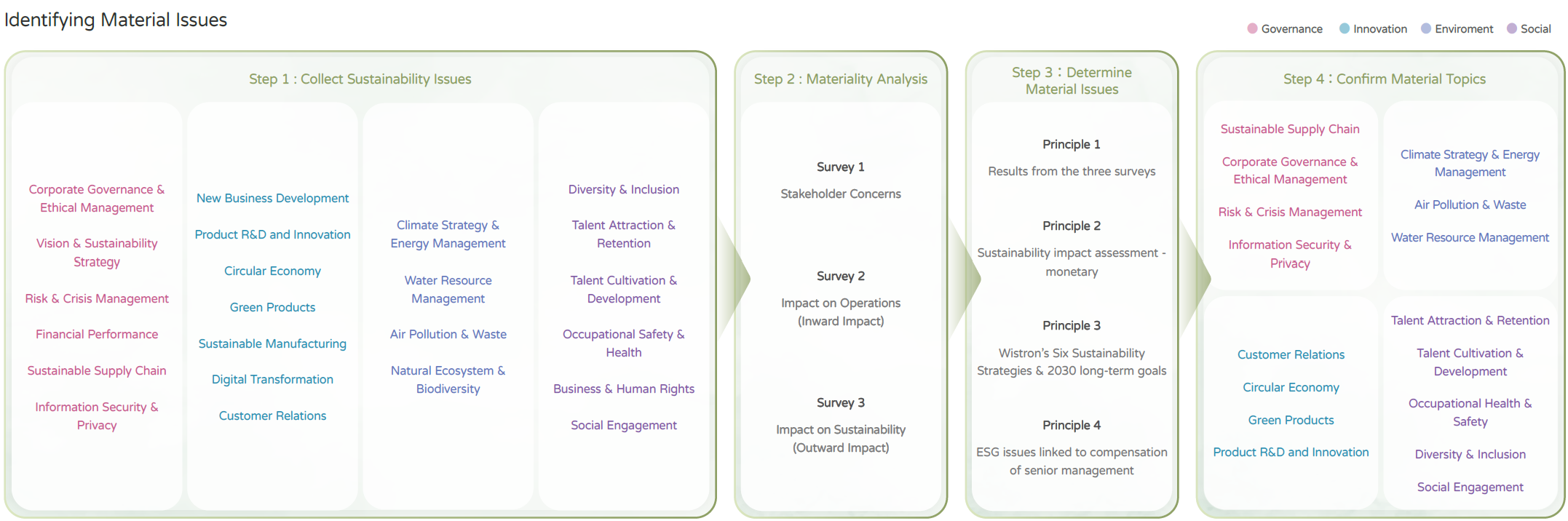
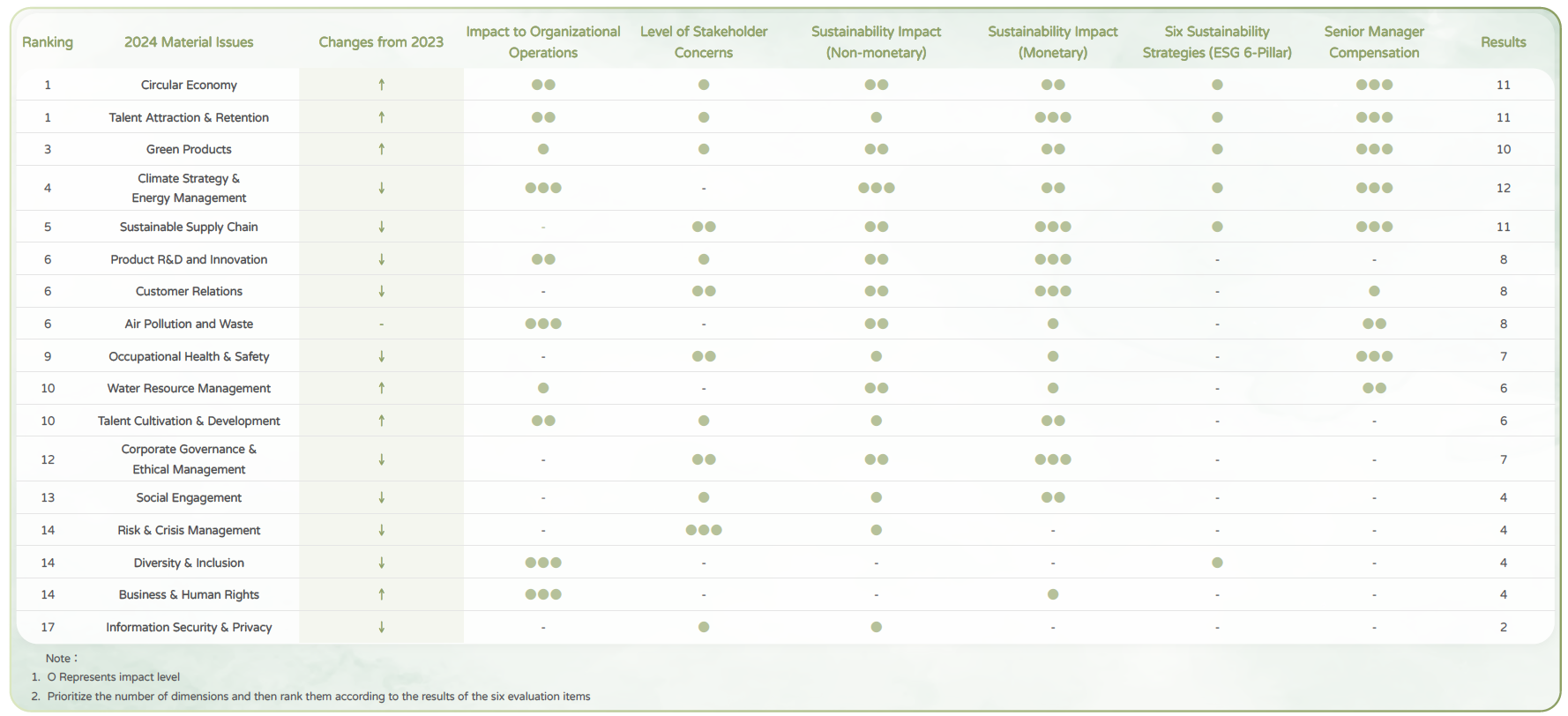
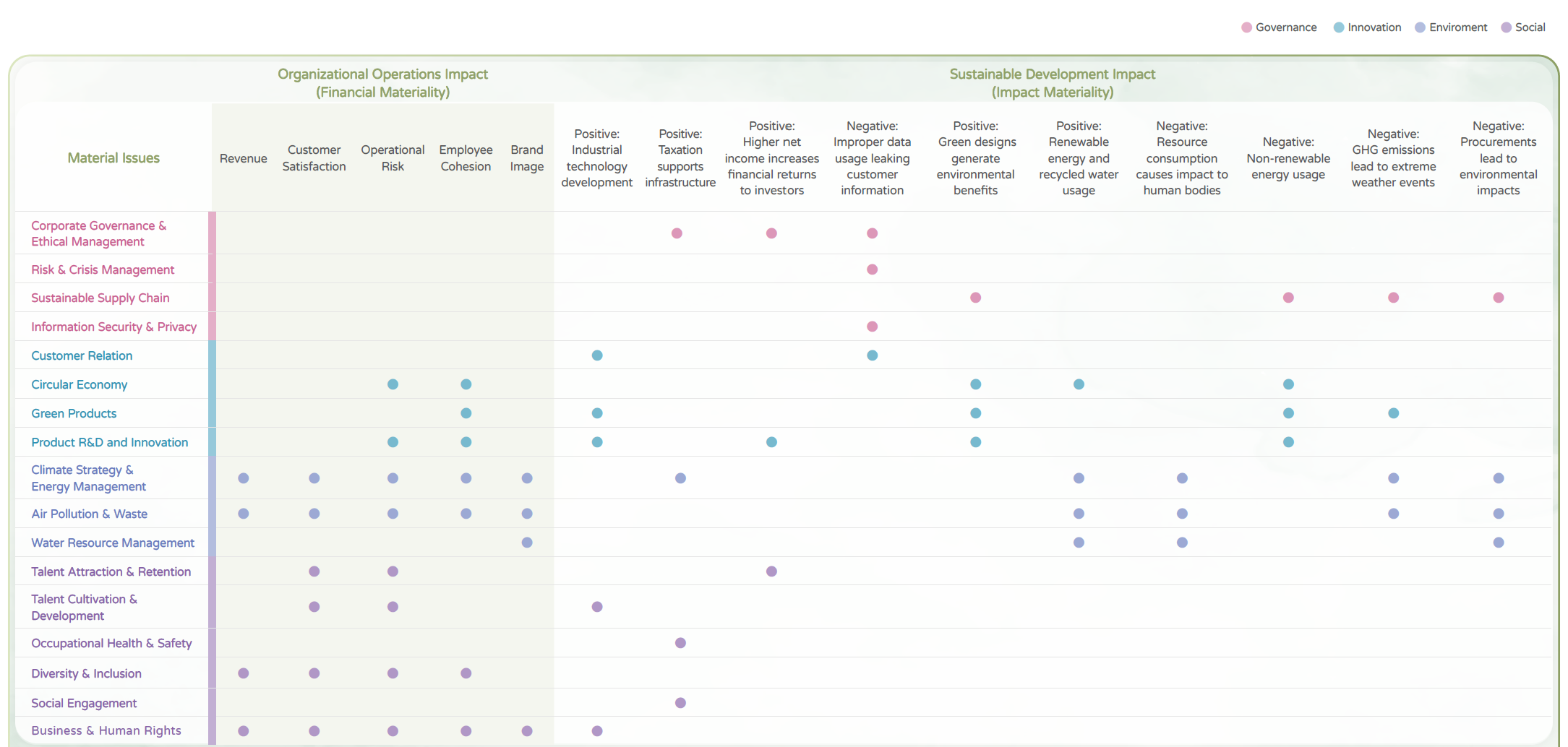
| Risk Type |
Description of Risk |
Mitigation Measures |
Severity |
Frequency |
Relevant Material Issue |
| Compliance |
Violation of environmental, health, and safety-related regulations (non-compliance with environmental and occupational safety laws) |
1. Regular regulatory audits
2. Develop occupational safety, health, and environmental policies and management systems in accordance with international standards, namely ISO 45001 and ISO 14001
|
3 |
2 |
- Corporate Governance & Ethical Management
- Occupational Health & Safety
|
| Strategy |
Sustainability-related investment projects result in negative ESG impacts or controversy |
Project management teams conduct risk control procedures both before and after investing |
3 |
2 |
- Corporate Governance & Ethical Management
- Risk & Crisis Management
|
| Compliance |
Failure to implement preventive and detective internal controls for legal compliance |
Regular review of existing systems and personnel to address and enforce regular audits and encourage personnel to comply with regulations |
3 |
2 |
- Corporate Governance & Ethical Management
- Risk & Crisis Management
|
| Strategy |
Failure to establish a risk mitigation response plan |
Develop and implement response plans to reduce risks |
2 |
1 |
|
| Strategy |
Board fails to identify and assess risks; senior managers fail to propose risk mitigation plans |
The Audit Committee assists the Board of Directors in fulfilling its risk management responsibilities, with the Board approving the company's risk management policies and related regulations. A Risk Management Team is established under the Audit Committee, comprising heads of each department as members. The Team collaborates with relevant operational units to implement effective risk management |
3 |
2 |
- Corporate Governance & Ethical Management
- Risk & Crisis Management
|
| Operational |
Suppliers fail to implement a comprehensive decarbonization plan |
1. Inventory supplier's carbon emissions
2. Review supplier's decarbonization plans
3. Set emission reduction targets for suppliers |
3 |
2 |
- Sustainable Supply Chain
- Climate Strategy & Energy Management
|
| Operational |
Suppliers fail to comply with CSR standards, including work hours affected by COVID-19, overseas labor, human rights concerns, etc. |
1. Include CSR review into supplier assessments
2. Regularly conduct supplier SAQ reviews
3. Develop dynamic supplier management system |
4 |
2 |
- Sustainable Supply Chain
- Business & Human Rights
|
| Operational |
Suppliers' employees lack cybersecurity awareness, including sending internal files through personal emails or clicking on suspicious emails in their corporate mailbox |
1. Create management systems and training to build a legal-compliance culture
2. Use CSR audits to verify information security processes and risk assessments
3. Implement data classification and protection policies (confidential information protection measures) |
3 |
3 |
- Sustainable Supply Chain
- Information Security & Privacy
- Risk and Crisis Management
|
| Strategy |
Decline in product or service capabilities, resulting in client's selecting other agents |
1. Regular employee training (on laws, product updates, and OEM requirements)
2. Continue to acquire OEM certification to enhance technical capability
3. Obtain OEM solution partner status to acquire new clients and retain existing ones |
3 |
1 |
- Product R&D and Innovation
- Customer Relations
|
| Strategy |
Failure to meet customer requirements in the cooperation process. For example, transferring production lines, R&D support, etc. |
1. Host weekly meetings with customers to confirm all tasks are in progress
2. Regularly communicate with management at customer companies to ask whether any improvements are required
3. Analyze root causes and develop prevention strategies in the event of customer complaints |
2 |
1 |
- Product R&D and Innovation
- Customer Relations
|
| Compliance |
Client-designed products infringe on third-party patents, leading to lawsuits |
1. Upon legal notice, liaise directly with client legal teams per contract terms and begin discussions on soliciting related litigation fees and guarantees
2. Provide regular legal training to prevent unintentional legal violations
3. Verify patent violations during quotation process if product requires new technologies |
5 |
2 |
- Customer Relations
- Product R&D and Innovation
- Information Security & Privacy
|
| Operational |
Employees lack awareness of privacy and data protection laws, leading to personal data leaks |
1. Establish and publish privacy policies
2. Company-wide awareness campaigns to ensure employees understand and follow privacy regulations
3. Privacy training courses to increase employee knowledge of privacy rights
4. Set up whistleblowing channels (phone/email) |
3 |
2 |
- Information Security & Privacy
- Talent Cultivation & Development
|
| Operational |
Lack of comprehensive information security management systems for third-party vendors |
Implement the published and updated "Third-party Information Security Management Guidelines" to strengthen information security management and control among suppliers across various stages, including supplier selection, tiered management, and regular security risk reviews |
3 |
3 |
- Information Security & Privacy
- Sustainable Supply Chain
|
| Strategy |
Lack of clear AI governance framework, structure, management processes, and protection mechanisms |
1. Review applicable regulations, international guidelines, adopted standards, and client requirements
2. Enhance AI lifecycle risk management |
4 |
3 |
- Information Security & Privacy
|
| Operational |
Lack of innovative thinking may hinder business growth over the next three to ten years |
1. Establish new business and forward-looking units; asses new technologies to adopt; and draft white papers to be reviewed quarterly and updated annually
2. Convert innovative technologies into intellectual property; a dedicated team was established in 2018 to promote related efforts |
3 |
2 |
- Product R&D and Innovation
|
| Compliance |
Insufficient supply of renewable energy and certificates. Due to increased production capacity at our sites, Scope 2 emissions have risen. Failure to procure sufficient renewable energy may thus hinder our emission reduction targets or fall short of customer expectations |
1. Assess and plan the actual renewable energy demand for each facility
2. Collaborate with third-party providers to purchase required renewable energy |
2 |
3 |
- Customer Relations
- Climate Strategy & Energy Management
|
| Compliance |
Droughts & floods |
1. Implement water management and daily water conservation measures
2. Set short-, mid-, and long-term goals and incorporate them into routine performance evaluations to effectively reduce water use per unit of revenue
3. Implement water recycling and wastewater management
4. Conduct scenario simulations and risk assessments for droughts and floods
5. Work with local water suppliers to implement special water supply mechanisms during droughts, in order to maintain plant operations |
3 |
1 |
- Climate Strategy & Energy Management
- Water Resource Management
|
| Compliance |
Improper waste disposal, recycling, or scrapping |
1. Implement waste sorting at the source
2. Engage certified professional waste processors for proper handling
3. Declare waste in compliance with related laws and conduct regular audits
4. Require waste transport vehicles to be equipped with GPS tracking systems |
3 |
4 |
- Air Pollution & Waste
- Sustainable Supply Chain
|
| Operational |
Failure to foster a diverse, equitable, and inclusive (DEI) workplace, leading to incidents of discrimination or harassment |
1. Dynamically adjust management mechanisms in accordance with legal requirements
2. Implement DEI policies, conduct anti-harassment /DEI training to raise awareness
3. Establish a grievance platform and designate dedicated personnel to handle and follow up with grievances |
3 |
4 |
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Business & Human Rights
- Talent Cultivation & Development
|
| Strategy |
Lack of employee understanding or alignment with corporate vision and mission, leading to weak adoption of core values |
1. Create a dedicated page on our official website to communicate the company’s vision, mission, and core values, and provide corresponding employee training
2. Host orientation programs such as the Core Values Workshop and Wi Talk sessions led by the CEO to promote management philosophy and values
3. Organize core value experiences to deepen employees’ understanding and alignment
4. Integrate core value indicators into the performance management system to assess employee's behavioral alignment with company values |
2 |
2 |
- Talent Attraction & Retention
- Talent Cultivation & Development
|
| Operational |
Lack of comprehensive employee communication channels |
1. Multiple employee communication channels have been established at headquarters and all office/factory sites
2. A global employee portal has been launched to deliver consistent and critical operational information |
3 |
2 |
- Talent Attraction & Retention
|
| Strategy |
Intensified demand and competition for talent in Taiwan's tech sector due to global economic shifts, especially for international professionals, leads to greater recruiting challenges |
1. Develop industry-academia collaboration programs to cultivate required skills and offer internships, enabling direct employment upon graduation
2. Strengthen employer branding and corporate image to attract suitable talents |
3 |
2 |
- Talent Attraction & Retention
- Diversity & Inclusion
|
| Operational |
Employees unfamiliar with codes of ethics or conduct, leading to violations such as bribery, discrimination, or harassment |
1. Establish and announce ethics policies and codes of conduct and ensure employees are familiar with these guidelines
2. Conduct annual employee training and signing on codes of conduct
3. Establish grievance handling and resolution procedures |
3 |
3 |
- Talent Attraction & Retention
- Talent Cultivation & Development
- Business & Human Rights
|
| Operational |
Training and development programs not aligned with organizational goals |
1. Define managerial competencies and provide corresponding training
2. Continuously improve onboarding and compliance training programs
3. Provide courses on industry-specific technologies, digital transformation, and ESG in response to trends
4. Develop training blueprints by business group and job function based on identified needs
5. Continue to develop self-development learning resources |
3 |
3 |
- Talent Cultivation & Development
|
| Compliance |
Failure to implement workplace safety measures as communicated, increasing the risk of incidents |
1. Set up diverse reporting channels
2. Implement holiday patrol and incident reporting by electrical mechanical personnel and security staff
3. Conduct regular emergency response drills (first aid, fire safety) |
3 |
3 |
- Occupational Health & Safety
- Talent Cultivation & Development
|
| Compliance |
Emergency response procedures not updated in line with international standards or local regulations; OSH plans remain incomplete |
1. Provide training on emergency response procedures
2. Establish emergency response management procedures
3. Undergo third-party external audits for validation |
2 |
3 |
- Occupational Health & Safety
- Corporate Governance & Ethical Management
|
| Compliance |
Overtime hours exceed the limit prescribed by labor law (46 hours/month) |
HR monitors weekly overtime hours and reminds departments to enforce proper labor management |
2 |
3 |
- Business & Human Rights
- Corporate Governance & Ethical Management
|
| Compliance |
Failure to review recruitment practices in light of regulatory changes; lack of communication and training on legal risks during hiring |
1. Standardize recruitment processes and adopt a unified recruitment platform, with SOPs for each stage
2. Regularly review recruitment and hiring policies for legal compliance
3. Provide regular training on common hiring mistakes and legal risks to enhance employer awareness and skills |
2 |
3 |
- Business & Human Rights
- Talent Attraction & Retention
- Talent Cultivation & Development
|
| Strategy |
Social investment at each site not linked to ESG policies |
Implement a system for compiling information so that offices and factories worldwide may regularly upload and review community development investment plans and implementation results. Compiled information will then be reported in the annual ESG report |
1 |
1 |
|
| Strategy |
Lack of well-planned social investment and donation efforts, resulting in missed opportunities to amplify corporate social impact through resource integration |
Develop and implement charitable donation and sponsorship guidelines, ensuring adherence and regularly reviewing execution results |
1 |
1 |
|